RAISING AWARENESS
We do not often talk about Brain Injuries. Millions of people are affected, many carry very important remains.
MENU
1 - Introduction
2 - The Brain 3 - Brain injuries 4 - Consequences of Brain Injury 5 - How you can contribute 1 - INTRODUCTION
Millions of people undergo a Brain Injury every year. It is estimated that more than 1.5 million people undergo a form of brain injury every year in the United States and Western Europe individually. Many recuperate relatively well and can undertake a normal life. A non negligible amount however carry lifetime remains. It is estimated that in the USA alone there are more than 5 million people that are carrying permanent disabling remains. There exist many different types of brain injuries, with different effects. Many people undergo a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) due to an accident. Approximately the same number undergo a Non-Traumatic Brain Injury, their brain is affected by an internal cause. The consequences of brain injuries vary from person to person and depending on the precise cause, though they can have many things in common. The most important difference is the level of affection of the person. Some recuperate living a normal life, where as some carry significant remains if able to undergo anything at all. The Brain Injury I suffered is called "Meningo Encephalitis", a non-traumatic brain injury. It is, in my case, a completely invisible illness with consequences that are very difficult for outsiders to imagine and understand. I myself still have difficulty completely understanding and explaining it. In short our brain normally uses approximately 30% of our energy. My brain probably uses 2 or 3 times more energy than normal. I therefore get tired very very fast and there are many consequences as soon as I do more than my body can handle.
I met someone that went to hospital almost at the same time as me. I spent 3 months in the hospital, he spent 18 months there. I am lucky to be able to speak all 4 languages and do all items I previously learned almost like before and am fit for long walking trips, ski, travel. He still has difficulty speaking his main language and is unable to do long distance walks. Some people recuperate less than either of us. He sadly in 2017 passed away.
From the little news that was transmitted, it appears that Michael Shumacher, the famous formula 1 driver, is still completely unable to communicate (he fell on his head when Skiing in winter 2014). I have since witnessed and met people with many other relevant cases. Many of the people that carry an important remain lack essentials. For this reason, one of the objectives is to get as many people as possible to FollowKevin and contribute to fundraising. I will send an email with you once every few weeks to share my pictures, my experience traveling and my story. What can you do to help?
The goal is to raise funds to support The Encephalitis Society, an organization based in the United Kingdom working in research into Encephalitis Brain Injuries. The society also interacts worldwide with patients that have suffered Encephalitis, providing them with information, essential help and care. This film is a good introduction to what it can mean to undergo a Brain Injury :
This film means a lot to me because it is relevant to what I have lived and am living though it is not exactly the same. We did not undergo the same kind of Brain Injury, but it is very pertinent. We all live something different though we also have many things in common and can understand each other much more than someone that has not lived something similar.
LINK TO THE TRAILER : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VSfpA3AEKmY It is possible to watch this movie on Netflix : www.netflix.com You have to pay to be member on Neflix, but the first month is for free, so it is possible to see this for free. 2 - The Brain - General information about the brain
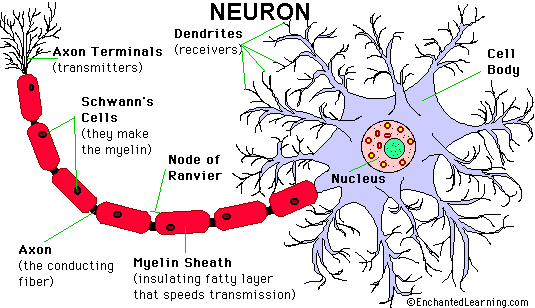
The brain is our primary control center, a fantastically complex organ containing billions of nerves that can simultaneously process information from our bodies, operate our internal organs, generate thoughts and emotions, store and recall memories, and control movement. Scientists have studied the brain for centuries and are nowhere near to fully understanding its intricacies. We now know relatively well which part of the brain does what. It is known because after assembly of scans of brain injuries and analysis of the deficits of each person it has become possible to get general knowledge about what part of the brain does what. It however remains very complex. We are all made differently. The number of human beings on planet earth (7 billion) is a detail compared to the number of items our individual brains contain and their interconnection. Our brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells (neurons). Each neuron may be connected to up to 10,000 other neurons, passing signals to each other via as many as 1,000 trillion synapses (junctions). It is the seat of perception, consciousness, thoughts, feelings and actions. It controls all important bodily functions Billions of dollars are now invested getting to better understand it. The investment is focused on Alzheimer and other most common items. The day that they will understand this better it will hopefully lead to making it possible to find solutions for other brain injuries. 3 - Brain injuries
What is an Acquired Brain Injury (ABI)?
An Acquired Brain Injury (ABI,) is damage to the brain that was not present at birth and is non-progressive. The two categories of ABI are Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Non-Traumatic Brain Injury. The two types of Acquired Brain Injury (ABI) : A Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) : where the cause was external such as an assault, a motor vehicle accident, sports injuries or a bicycling accident. Non-Traumatic Brain Injury: where the cause was an internal problem such as an infection (e.g. meningitis or encephalitis), a stroke, an aneurysm (i.e. a swollen or ruptured blood vessel in the brain), or a tumor. Such illnesses affect approximately one person out of 250 each year (depending on source). This means more than 1.5 million people in Western Europe and the USA individually. While the majority of people who experience a brain injury (especially soft traumatic ones) are able to relatively quickly return to their daily lives, it is also a large number of the concerned people that become permanently disabled. The most relevant number I found related to this is that more than 5 million Americans are living today with disability related to brain injury. It is estimated that there occur as many Non-Traumatic Brain Injuries as Traumatic ones. In Europe and the USA, this costs the governments hundreds of billions of dollars each year. Possible causes of Non-Traumatic Brain Injuries Anoxic injuries (Lack of oxygen to the brain) – Near drowning – Suffocation – Choking Vascular injuries (Disruption in blood supply to the brain) – Stroke (blocked blood vessel in the brain) – Aneurysm (broken blood vessel in the brain) Inhalation of ingestion of toxic substances – Sniffing glue, paint, or carbon monoxide – Drug use Immune Deficiency – Meningitis (inflammation of the meninges) – anyone is at risk to get this though it is relatively rare. – Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) – anyone is at risk to get this though it is relatively rare 4 - CONSEQUENCES OF BRAIN INJURY (ABI)
The Effects of an ABI
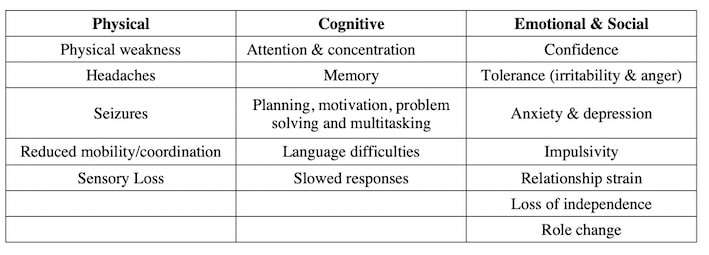
The consequences of a brain injury depend on the severity of the injury and the affected area. The most evident is if the person is in hospital and very limited in what can do (if able to do anything at all). In the long term some keep very important remains and are unable to do much. Others, have difficulty doing doing exercises, walking, etc. In addition to visible disabilities, there are many so-called invisible deficits that others do not often see at first. Although the causes of brain injury differ, the effects of these injuries on a person’s life are in a certain way quite similar. However, no two persons can expect the same outcome or resulting difficulties. The brain controls every part of human life: physical, intellectual, behavioral, social and emotional. The severity of such an injury may range from "mild," i.e., a brief change in mental status or consciousness to "severe". There exist several levels of impact of Brain injuries depending on many factors : - do not survive - completely out of service / unconscious (can be temporary, last years or be definite) - conscious but unable to be independent / need assistance. - recuperate essentials to live independently but 100 % out of work. Many side effects. - able to do a lot like before / are independent but get tired fast and many side effects. - recuperate almost 100%, able to have a relatively normal life. - fully recuperate For the first levels it is very evident for outsiders to see the impact, For the ones that recuperate reasonably well but not completely then it is much more difficult to see and understand. Invisible disabilities are often described by those involved as the heaviest burden after brain injury. After a stroke or trauma, certain disorders engines fail to be overcome. More elusive, invisible disabilities may instead be a challenge for a lifetime. Invisible deficits vary from one person to another. The following examples do not apply to everyone and are not exhaustive. Neurofatigue
Neurofatigue means that the victim will tire easily after any activity. It is one of the most debilitating consequences of a brain injury, as it influences everything the injured person does, both physically and mentally. In the early days, the ABI survivor is likely to find that they will tire easily after any activity, even chatting to friends or watching television, but particularly after tasks that require concentration or physical effort. This can be very depressing, particularly if the individual is aware of this change. They will often try to push themselves to complete a task in the belief that they might overcome their fatigue. This is seldom the right thing to do as it can lead to increased fatigue in the long-term. It takes time to build up energy. Taking rest periods both in between activities and when feeling tired is essential. Sleeping disorders Many brain injured suffer from sleeping disorders as well. Unfortunately, brain injury can often lead to a sleep disorder. The American Academy of Neurology reports that as many as 40 to 65 percent of people with mild traumatic brain injury complain of insomnia. After a brain injury many find it not only difficult to sleep, but they are very easily awakened, sometimes dozens of times a night. Sleep will usually be very light, so the smallest noise brings the person instantly awake. Many of the people that carry an important remain lack essentials.
For this reason, one of the objectives is to get as many people as possible to FollowKevin and contribute to fundraising. I will send an email with you once every few weeks to share my pictures, my experience traveling and my story. 5 - How you can Contribute
PASS THIS LINK TO OTHER PEOPLE :
= to help enlarge the network of possible contributors. Pass it on to anyone that might be interested in following this trip : - Forward them the email you received - or Send them the link : www.FollowKevin.org
Sources of Information : Important sources of information I used and where a lot of the data comes from for the above text :
- http://www.acquiredbraininjury.com/ - http://www.internationalbrain.org/brain-injury-facts/ - http://www.nln.ie/Community-Based-Rehab/Quest-brain-injury-services/What-is-an-ABI-.aspx - http://www.brainline.org - http://www.biasd.ca/education/causes-of-abi/ - http://www.braininjuryhub.co.uk/information-library/non-traumatic I use the opportunity to here mention the fact that due to my fatique I rarely have the energy to do a lot of reading or write long text myself. Therefore, a lot of the information on this website and on all my albums is copy paste from other sources with some modifications. When I talk about the history or other general information it is often a summarised copy / paste from websites such as wikipedia. |